Categorical data is data that classifies an observation as belonging to one or more categories. For example, an item might be judged as good or bad, or a response to a survey might includes categories such as agree, disagree, or no opinion. Statgraphics includes many procedures for dealing with such data, including modeling procedures contained in the sections on Analysis of Variance, Regression Analysis, and Statistical Process Control.
| Procedure | Statgraphics Centurion 18/19 | Statgraphics Sigma express |
Statgraphics stratus |
Statgraphics Web Services |
StatBeans |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tabulation |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Donut Chart |  |
||||
| Frequency Tables |  |
 |
 |
||
| Crosstabulation |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Contingency Tables |  |
 |
 |
||
| Median Polish |  |
||||
| Correspondence Analysis |  |
||||
| Multiple Correspondence Analysis |  |
||||
| Likert Plot |  |
||||
| Item Reliability Analysis |  |
||||
| Tornado and Butterfly Plots |  |
||||
| Venn and Euler Diagrams (V19 only) |  |
The Tabulation procedure is designed to summarize a single column of attribute data. It tabulates the frequency of occurrence of each unique value within that column. The frequencies are displayed both in tabular form and graphically as a barchart or piechart.
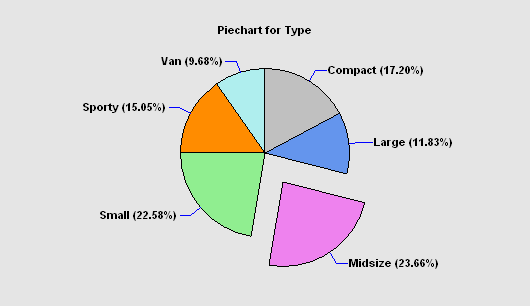
More: Tabulation.pdf
The Piechart / Donut Chart procedure plots a column of counts or frequencies using slices of a pie or sections of a donut. If desired, a selected slice may be offset from the rest of the pie or donut.
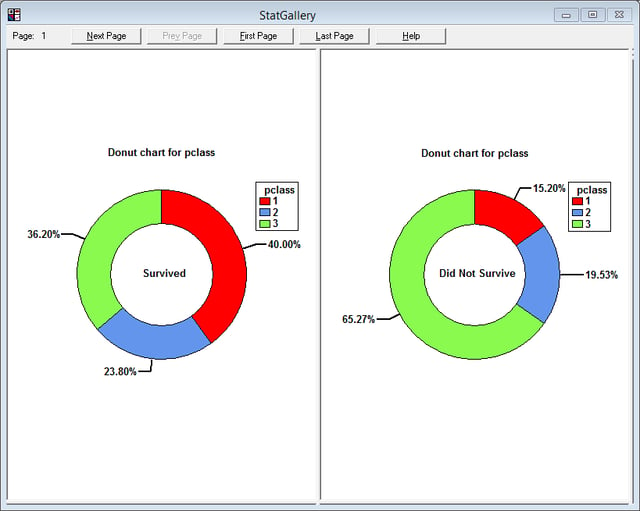
More: Piechart/Donut Chart.pdf or Watch Video
The Frequency Tables procedure analyzes a single categorical factor that has already been tabulated. It displays the frequencies using either a barchart or piechart. Statistical tests may also be performed to determine whether the data conform to a set of multinomial probabilities.
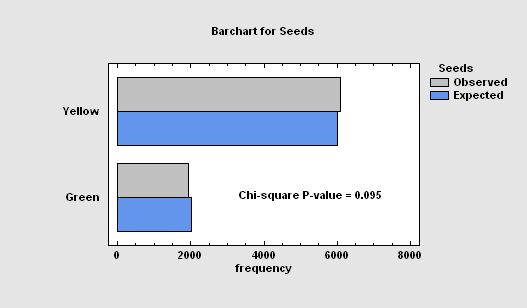
More: Frequency Tables.pdf
The Crosstabulation analysis procedure is designed to summarize two columns of attribute data. It constructs a two-way table showing the frequency of occurrence of all unique pairs of values in the two columns. Statistics are constructed to quantify the degree of association between the columns, and tests are run to determine whether or not there is a statistically significant dependence between the value in one column and the value in another. The frequencies are displayed both in tabular form and graphically as a barchart, mosaic plot, or skychart.
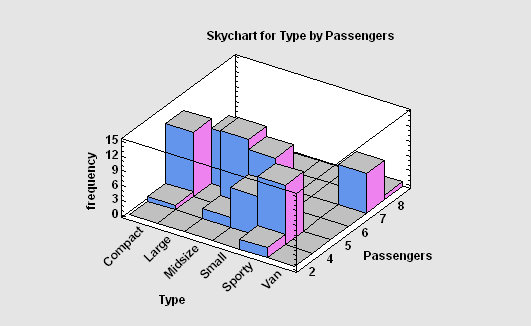
More: Crosstabulation.pdf
The Contingency Tables procedure is designed to analyze and display frequency data contained in a two-way table. Such data is often collected as the result of a survey. Statistics are constructed to quantify the degree of association between the rows and columns, and tests are run to determine whether or not there is a statistically significant dependence between the row classification and the column classification. The frequencies are displayed both in tabular form and graphically as a barchart, mosaic plot, or skychart.
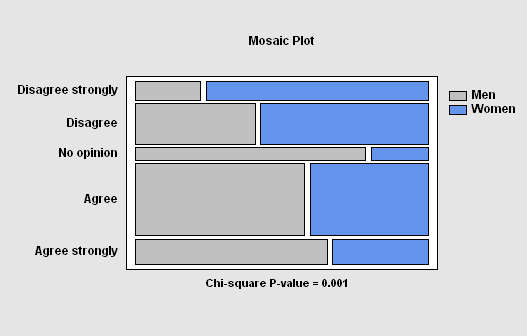
More: Contingency Tables.pdf
The Median Polish procedure constructs a model for data contained in a two-way table. The model represents the contents of each cell in terms of a common value, a row effect, a column effect, and a residual. Although the model used is similar to that estimated using a two-way analysis of variance, the terms in the model are estimated using medians rather than means. This makes the estimates more resistant to the possible presence of outliers.
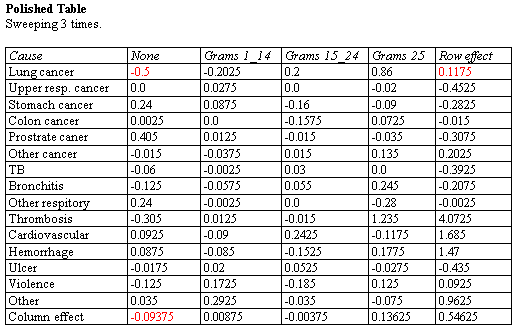
More: Median Polish.pdf
The Correspondence Analysis procedure creates a map of the rows and columns in a two-way contingency table for the purpose of providing insights into the relationships amongst the categories of the row and/or column variables. Often, no more than two or three dimensions are needed to display most of the variability or “inertia” in the table. An important part of the output is a correspondence map on which the distance between two categories is a measure of their similarity.
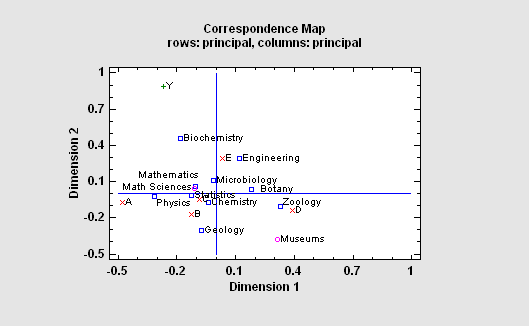
More: Correspondence Analysis.pdf
The Multiple Correspondence Analysis procedure creates a map of the associations among categories of two or more variables. It generates a map similar to that of the Correspondence Analysis procedure. However, unlike that procedure which compares categories of each variable separately, this categorical data analysis procedure is concerned with interrelationships amongst the variables. For a complex map such as that to the right, the Statgraphics dynamic rotate, zoom and pan operations can be very helpful.
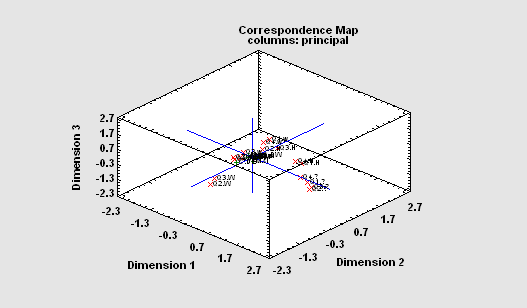
More: Multiple Correspondence Analysis.pdf
The Likert Plot procedure analyzes data recorded on a Likert scale. Likert scales are commonly used in survey research to record user responses to a statement.
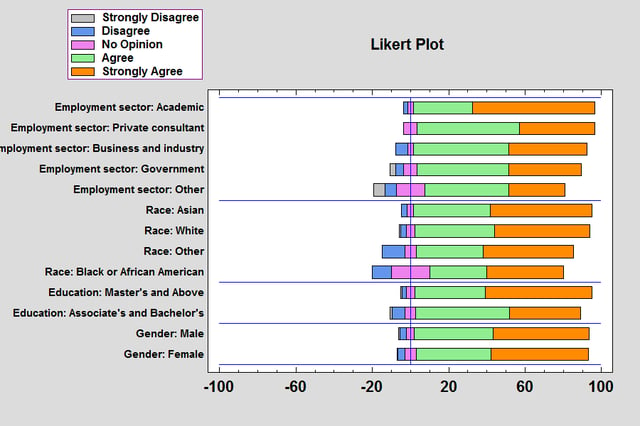
More: Likert Plot.pdf or Watch Video
The Item Reliability Analysis is designed to estimate the reliability or consistency of a set of variables. It is commonly used to assess how well a set of questions in a survey, each of which is designed to illicit information about the same characteristic, give consistent results. The major output of the procedure is Cronbach’s alpha.
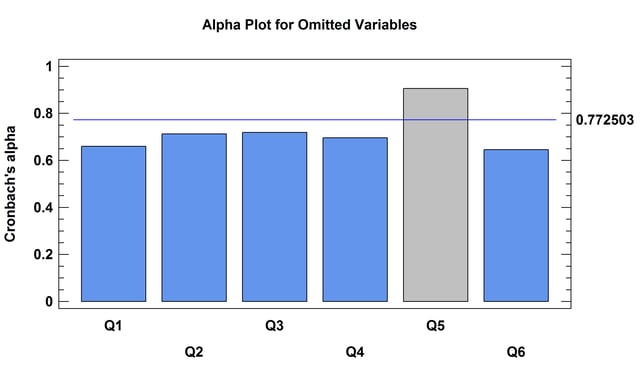
More: Item Reliability Analysis.pdf
Tornado and Buttefly Plots
The Tornado and Butterfly Plots procedure creates two similar plots that compare 2 samples of attribute data. Each plot consists of 2 sets of bars that show the frequency distribution of each sample over a set of categories. The only difference between the plots is where the labels are placed.
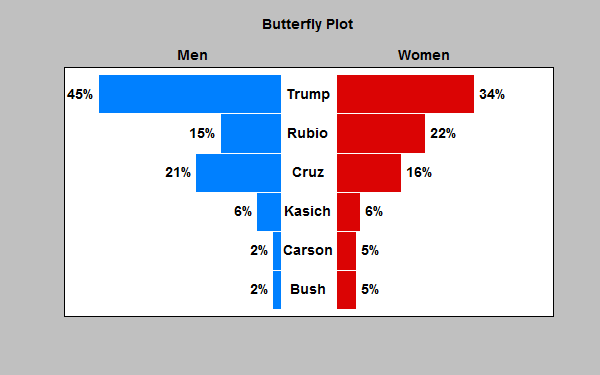
More: Tornado and Butterfly Plots.pdf or Watch Video
Venn and Euler Diagrams (Version 19)
The Venn and Euler Diagrams procedure creates diagrams that display the relative frequency of occurrence of discrete events. They consist of circular regions that represent the frequency of specific events, where the overlap of the circles indicates the simultaneous occurrence of more than one event.
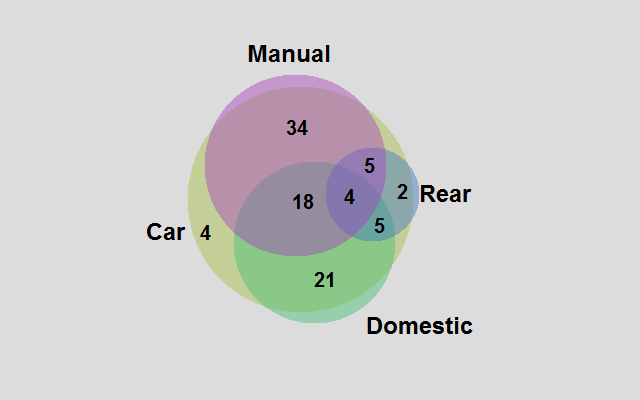
More: Venn and Euler Diagrams.pdf or Watch Video

© 2025 Statgraphics Technologies, Inc.
The Plains, Virginia
CONTACT US
Have you purchased Statgraphics Centurion or Sigma Express and need to download your copy?
CLICK HERE